Evolving Space Observation Equipment: From Ancient Observations to Cutting-Edge Telescopes
The evolution of space observation equipment represents an awe-inspiring journey that spans millennia. From humble beginnings of stargazers peering at the night sky to the high-tech telescopes and observatories of today, our quest to understand the universe has been marked by innovation, discovery, and technological advancement. In this blog post, we embark on a captivating journey through time to explore the development of space observation equipment, tracing the evolution from ancient civilizations to the present era of cutting-edge telescopes.
Ancient Observations: The Dawn of Stargazers
The Antikythera Mechanism (150-100 BC)
Our journey begins in ancient Greece, a civilization that has greatly contributed to the world of science and technology. One of the most remarkable inventions of this period is the Antikythera Mechanism, a mysterious device dating back to the second century BC. The device is considered one of the earliest examples of an astronomical calculator, which has brought about tremendous advancements in the field of astronomy. Discovered in a shipwreck, this complex mechanical calculator is a true testament to the ingenuity of the ancient Greeks. The Antikythera Mechanism was able to predict celestial events such as lunar and solar eclipses and the positions of planets, which greatly aided in the study of the cosmos and the development of scientific theories.
Astrolabe (2nd Century AD)
The astrolabe, which was invented in classical antiquity, was an essential tool for early astronomers and navigators. This portable device allowed users to measure the altitude of celestial objects and determine their positions in the sky. Additionally, the astrolabe was used by early astronomers and navigators for a variety of other purposes, such as calculating the time of day and determining the latitude of a location. It was also used for surveying and mapping, as well as for astrological purposes. In fact, the astrolabe was so important that it remained in use for centuries and was even used by famous astronomers such as Galileo Galilei and Johannes Kepler. Despite the fact that modern technology has made the astrolabe largely obsolete, it remains an important part of the history of astronomy and navigation.
Medieval Marvels: Arabic Innovations
Al-Battani’s Zij (9th Century AD)
During the Islamic Golden Age, from the 8th to the 14th century, Islamic scholars made remarkable progress in various fields, including astronomy. Al-Battani, a renowned scholar of the time, made significant contributions to this field. He is best known for his book “Zij,” an astronomical handbook that provided highly accurate data on the positions of stars, planets, and the moon. The book was so groundbreaking that it was used as a reference for centuries to come.
Apart from Al-Battani, other scholars like Ibn al-Haytham, Al-Farabi, and Al-Khwarizmi also made significant contributions in the field of astronomy during this period. Ibn al-Haytham, for example, is known for his work on optics and his studies on the behavior of light. Al-Farabi, on the other hand, was an expert on Aristotelian philosophy and made significant contributions to the field of metaphysics. Lastly, Al-Khwarizmi is known for his work on algebra and for introducing the Indian numerical system, which is widely used today.
The Islamic Golden Age was a time of great intellectual advancement, and the contributions of scholars like Al-Battani, Ibn al-Haytham, Al-Farabi, and Al-Khwarizmi played a significant role in shaping modern science and technology.
Alhazen’s Work on Optics (11th Century AD)
Ibn al-Haytham, also known as Alhazen, was a prominent scholar who made significant contributions to the field of optics. His pioneering work laid the foundation for understanding the nature of light and vision. Through his experiments, he was able to explain how light travels in straight lines and how it reflects off surfaces. He also developed the concept of refraction, which explains how light bends when it passes through materials of different densities.
Alhazen’s work on optics was not only groundbreaking, but it also had a lasting impact on the field of astronomy. His discoveries and theories influenced the development of telescopes, which were used to observe and study the stars and planets. In fact, many of the principles that Alhazen established in the 11th century are still used by scientists today in the fields of optics and astronomy.
It is also worth noting that Alhazen’s contributions to science were not limited to optics. He also made significant strides in the fields of mathematics and physics. His work on the laws of motion and the nature of light helped pave the way for future scientific discoveries. Overall, Ibn al-Haytham was a remarkable scholar who played a critical role in advancing our understanding of the natural world.
The Renaissance Revolution: Telescopes and Galileo Galilei (17th Century)
Galileo’s Telescope (1609)
In the early 17th century, Galileo Galilei made a groundbreaking discovery that would change the course of astronomy forever. He was the first person to use a telescope for astronomical observations, and this allowed him to see the cosmos in an entirely new way. Through his observations, Galileo discovered the moons of Jupiter, which were previously unknown to humanity. He also observed the phases of Venus and the craters on the Moon, which provided evidence against the geocentric model of the universe. This discovery was a turning point in human history as it challenged the prevailing beliefs of the time and paved the way for new developments in science and technology. Galileo’s work laid the foundation for modern astronomy and inspired countless scientists and astronomers to continue exploring the mysteries of the universe.
The Age of Refinement: Reflecting and Refracting Telescopes (18th-19th Centuries)
Herschel’s Reflecting Telescope (1789)
Sir William Herschel was an astronomer who made numerous contributions to the field. One of his most significant contributions was his work with reflecting telescopes. Herschel’s research with these telescopes led to many discoveries that expanded our understanding of the universe. For example, he detected the planet Uranus, which was a groundbreaking discovery at the time. Herschel also discovered several moons and was the first to identify binary star systems, which are two stars that orbit around each other. These discoveries were groundbreaking and had a significant impact on our understanding of the cosmos.
Clark’s Refracting Telescopes (19th Century)
Alvan Clark was an American astronomer and telescope maker who lived in the 19th century. Along with his sons, he produced some of the finest refracting telescopes of their time. Their instruments were highly sought after by astronomers and were used for groundbreaking observations. For example, in 1846, Johann Gottfried Galle used a telescope made by Alvan Clark & Sons to discover the planet Neptune. The discovery was a major achievement in the field of astronomy and helped to expand our understanding of the solar system. In addition to this, Clark’s telescopes were also used to study double stars, which are crucial to our understanding of the universe and how it works. By observing double stars, astronomers were able to learn more about the properties of stars and how they interact with each other. Overall, Alvan Clark and his sons made significant contributions to the field of astronomy through their high-quality telescopes and the groundbreaking observations that were made using them.
Twentieth Century Advancements: Radio Telescopes and Space Observatories (20th Century)
The Birth of Radio Astronomy (1930s)
Radio telescopes, which were first pioneered by Karl Jansky in 1931, and later by Grote Reber in 1937, have been instrumental in expanding our understanding of the universe. By detecting radio waves emitted by celestial objects, these telescopes have allowed us to explore a previously unknown aspect of space. With radio telescopes, astronomers have been able to detect a variety of phenomena, including cosmic microwave background radiation and pulsars, which have provided us with valuable insights into the origins and workings of the universe.
The discovery of cosmic microwave background radiation, which was first detected in 1964 by Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson, has been particularly significant. This radiation is thought to be the residual heat left over from the Big Bang, and its discovery has helped us to further refine our understanding of the origins of the universe. Similarly, the discovery of pulsars has provided us with valuable insights into the properties of neutron stars and the nature of gravity.
In addition to these groundbreaking discoveries, radio telescopes have also been used to study a wide range of objects and phenomena in space, including black holes, galaxies, and the interstellar medium. By continuing to explore the universe using radio telescopes, we can expect to uncover even more exciting discoveries in the future.
Hubble Space Telescope (1990)
Launched in 1990, the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) revolutionized space observation by capturing breathtaking images and conducting groundbreaking research. The telescope has been instrumental in advancing our knowledge of the universe, providing us with stunning images that have helped us to understand the cosmos in a more profound way. The HST has been used to study the origins of the universe, the formation of galaxies, and the evolution of stars, among other things. It has also been used to detect and study exoplanets, providing us with valuable information about the possibility of life beyond our solar system. In addition to its scientific achievements, the HST has captured the public’s imagination and inspired a new generation of space enthusiasts. Its images and discoveries have been featured in countless books, articles, and documentaries, and the telescope has become a symbol of humanity’s curiosity and desire to explore the unknown.
The Present and Beyond: Cutting-Edge Space Observation Equipment
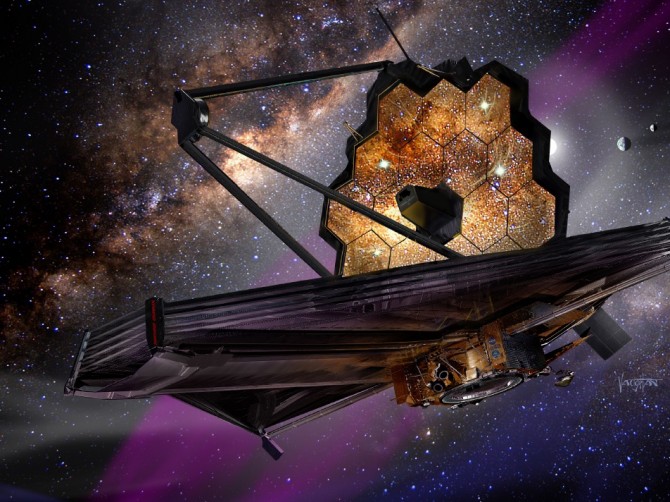
James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a much-awaited space telescope that was launched aboard an Ariane 5 rocket from Kourou, French Guiana, on December 25, 2021, and landed at the Sun-Earth L2 Lagrangian point in January 2022. The JWST is considered the successor to the Hubble Space Telescope and operates in the infrared spectrum, allowing it to peer through the dust and gas clouds that obstruct visible light. It is expected to provide a wealth of new insights into the early universe, exoplanets, and other celestial objects.
At a press conference attended by US President Joe Biden on July 11, 2022, the first official image of the James Webb Space Telescope was released to the public. The image depicts a section of the Carina Nebula, one of the most massive star-forming regions in our galaxy. The JWST’s advanced technology allowed it to capture a clearer and more detailed image than ever before, providing astronomers with a new perspective on this fascinating phenomenon.
With its advanced capabilities, the JWST is expected to answer many of the unknown questions that have been plaguing astronomers for years. For example, it will allow scientists to study the formation of the first galaxies and stars in the universe, as well as the evolution of galaxies over time. It will also enable us to study exoplanets in greater detail, potentially revealing the presence of life beyond our solar system. Overall, the James Webb Space Telescope represents a major breakthrough in our understanding of the universe and promises to provide us with many exciting discoveries in the years to come.

Ground-Based Observatories with Advanced Instruments
Modern ground-based observatories have been instrumental in expanding our knowledge of the universe. With their state-of-the-art instruments, including adaptive optics and interferometry, these observatories have pushed the boundaries of what we can observe from Earth. As a result, we have been able to make significant discoveries in exoplanet research, black hole studies, and the mapping of the cosmic microwave background. For example, the use of adaptive optics has allowed us to see distant objects with much greater clarity than ever before, revealing previously unknown details about the universe. In addition, interferometry has enabled us to combine the light from multiple telescopes, increasing our ability to study the cosmos in greater detail. With continued advancements in technology, ground-based observatories will undoubtedly play a vital role in expanding our understanding of the universe for years to come.
Conclusion: A Journey Through Space and Time
The evolution of space observation equipment is a fascinating topic that reflects humanity’s unceasing quest to unravel the mysteries of the universe. Throughout history, humans have been fascinated by the stars and the cosmos. Ancient civilizations used their knowledge and ingenuity to create instruments that would allow them to observe the skies. These instruments included the astrolabe, which was invented by the Greeks, and the armillary sphere, which was developed in China.
As technology advanced, so did our ability to observe the universe. The invention of the telescope in the early 17th century revolutionized astronomy, and allowed us to see further into space than ever before. Since then, scientists have continued to innovate and develop new tools for observing the cosmos. The Hubble Space Telescope, for example, has provided us with breathtaking images of galaxies, stars, and other celestial objects. Ground-based observatories, such as the Keck Observatory in Hawaii, have also played an important role in our understanding of the universe.
Looking to the future, there is no doubt that space observation equipment will continue to evolve and improve. New technologies, such as the James Webb Space Telescope, which is set to launch in 2021, will allow us to see even further back in time, and provide us with a greater understanding of the universe’s origins. As we explore the cosmos, the story of space observation equipment reminds us of the boundless potential for discovery that lies beyond the stars, and the limitless possibilities that await us as we continue to push the boundaries of science and technology.