The Shrinking of Mercury: A Celestial Puzzle
Introduction
The innermost planet of our solar system, Mercury, has always fascinated astronomers and scientists. It’s not just the scorching temperatures or the lack of a substantial atmosphere that piques their interest. One of the most intriguing aspects of Mercury is its continual shrinkage, and in this article, we will delve into the celestial puzzle of why Mercury is shrinking.
1. The Basics of Mercury
Mercury, the closest planet to the Sun, is a fascinating celestial body in our solar system. It is a rocky and terrestrial world, similar to Earth in many ways. With a diameter of about 4,880 kilometers (about 3,032 miles), Mercury may seem small compared to other planets, but it holds great scientific significance.
One of the most remarkable features of Mercury is its extreme temperature variations. During the day, the surface of the planet can heat up to scorching temperatures, reaching up to 430 degrees Celsius (800 degrees Fahrenheit). This intense heat is due to its close proximity to the Sun, where it is exposed to intense solar radiation. However, as the Sun sets, Mercury experiences a dramatic drop in temperature, plunging to a bone-chilling -180 degrees Celsius (-290 degrees Fahrenheit) during the night.
These extreme temperature fluctuations on Mercury pose unique challenges for any potential exploration or colonization efforts. The intense heat during the day can make it difficult for any spacecraft or equipment to withstand such extreme conditions. On the other hand, the freezing temperatures at night present their own set of obstacles. Finding a way to regulate and maintain a habitable environment on Mercury would require innovative technologies and careful planning.
Despite its harsh conditions, scientists and researchers continue to study Mercury to unravel its mysteries and gain valuable insights into the formation and evolution of our solar system. The extreme temperature variations on this small planet provide a unique opportunity to study the effects of such extreme conditions on planetary bodies.
In conclusion, Mercury, with its small size and extreme temperature variations, is a captivating world that offers a wealth of scientific knowledge waiting to be discovered. Exploring this rocky planet further will undoubtedly lead to new discoveries and a deeper understanding of the complexities of our solar system.

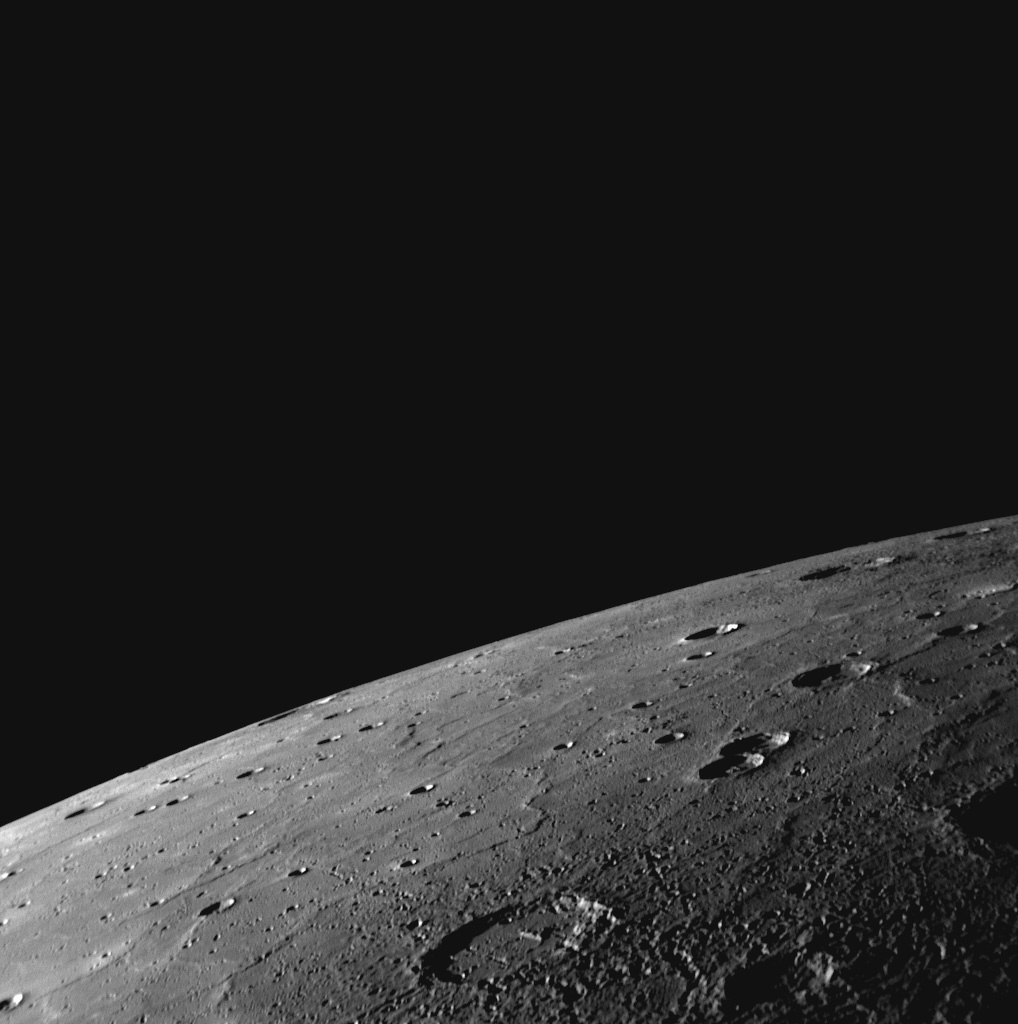
2. The Discovery of Shrinkage
The notion that Mercury is contracting or shrinking has been widely discussed and studied for many decades. This fascinating concept gained further credibility and confirmation in the 1970s when NASA’s Mariner 10 spacecraft conducted detailed observations. The groundbreaking Mariner 10 mission not only granted us the privilege of witnessing the first close-up images of Mercury but also uncovered a remarkable revelation. The spacecraft’s images unveiled a plethora of fault scarps, resembling majestic cliffs or ridges, scattered across the planet’s surface. These awe-inspiring geological features provided undeniable and compelling evidence supporting the theory of global contraction. The invaluable insights gained from the Mariner 10 mission have significantly deepened our understanding of Mercury’s geological history and continue to fascinate scientists to this day.
3. Cooling Down and Its Consequences
The primary reason behind Mercury’s shrinkage is its interior cooling down. Unlike Earth, which has a relatively active geological system driven by plate tectonics, Mercury has a single, rigid outer shell. As the planet cooled after its formation, this outer shell began to contract, causing its surface to wrinkle and fold. This process of contraction and wrinkling is known as tectonic activity. Over millions of years, these geological processes shaped the surface of Mercury, creating its unique features such as scarps, ridges, and cliffs. These features provide valuable insights into the planet’s history and give scientists clues about its formation and evolution. Understanding the geological history of Mercury is crucial for unraveling the mysteries of our solar system and gaining a deeper understanding of how planets form and change over time.
4. The Role of Contraction Features
One of the most compelling pieces of evidence supporting the fact that Mercury has undergone contraction over time is the presence of distinct geological features known as lobate scarps. These fascinating scarps are essentially elongated cliffs that exhibit a curved or lobate shape, and they can span for miles in length and reach heights of hundreds of feet. These scarps form as a result of the compression that occurs due to the planet’s contraction, and the sheer abundance of these features scattered across Mercury’s surface serves as additional concrete evidence of this intriguing phenomenon. It is truly remarkable to observe how these lobate scarps provide us with valuable insights into the geological evolution and dynamic nature of Mercury throughout its history.

5. The Implications for Mercury
Mercury’s continuous shrinkage has several significant implications for the planet. Firstly, as the planet undergoes shrinkage, it experiences a gradual compression and deformation of its surface. This ongoing process has fascinating consequences, as it gives rise to the formation of various intriguing geological features that we observe on the planet. These features, such as impact craters, volcanic plains, and scarps, offer valuable insights into the planet’s history and geological activity.
Secondly, the continuous shrinkage of Mercury also plays a crucial role in the buckling and cracking of its crust. This phenomenon leads to the creation of a remarkable network of cliffs and ridges, which are visible on the planet’s surface. These geological formations, known as lobate scarps, are evidence of the planet’s tectonic activity and the ongoing stresses and strains that it experiences.
In summary, the continuous shrinkage of Mercury not only results in the compression and deformation of its surface, giving rise to various geological features, but it also contributes to the formation of cliffs and ridges through the buckling and cracking of the planet’s crust. These geological processes provide valuable insights into Mercury’s history and its dynamic nature.
6. Mercury’s Tenuous Atmosphere
Mercury’s atmosphere, or rather the lack of it, plays a significant role in the planet’s shrinkage. The absence of an atmosphere means that there is no protective layer to insulate the planet from the extreme temperature variations it experiences between day and night. As a result, the rocks on the surface undergo a daily process of expanding and contracting, which further aggravates the overall contraction of the planet. This constant expansion and contraction cycle due to the absence of insulation greatly contributes to the gradual shrinkage of Mercury over time.
7. Looking to the Future
As we continue to study Mercury and other celestial bodies, we gain valuable insights into the evolution of planets and the processes that shape their features. This knowledge is crucial for understanding the vast universe and the mysteries it holds. By exploring Mercury’s peculiar characteristics, scientists have the opportunity to delve deeper into the geological and thermal history of rocky planets, unraveling the secrets of their formation and development over time. Through extensive research and analysis, we can uncover fascinating details about the forces that have shaped our solar system and the countless worlds within it. The exploration of Mercury opens up new avenues of scientific discovery, expanding our understanding of the cosmos and our place within it.
In conclusion, the ongoing reduction in size of Mercury is a celestial puzzle that has captivated the scientific community for many years. Scientists have been fascinated by the unique geological features, extreme temperature conditions, and the absence of a significant atmosphere, all of which play a role in this intriguing phenomenon. As we continue to delve deeper into the exploration and understanding of our solar system, the mysterious phenomenon of Mercury’s continual shrinkage continues to be an enthralling and captivating subject of scientific investigation and study.