The Hazard of Space Debris: A Cosmic Perspective
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- 1.1 The Growing Threat of Space Debris
- 1.2 The Origins of Space Debris
- Understanding Space Debris
- 2.1 What is Space Debris?
- 2.2 The Lifecycle of Space Debris
- The Dangers of Space Debris
- 3.1 Collisions in Orbit
- 3.2 The Kessler Syndrome
- 3.3 The Threat to Satellites
- Mitigating Space Debris
- 4.1 Tracking and Monitoring
- 4.2 Deorbiting and Removal
- 4.3 International Cooperation
- The Future of Space Debris
- 5.1 Space Sustainability
- 5.2 The Role of Space Agencies
- 5.3 Conclusion
1. Introduction
1.1 The Growing Threat of Space Debris
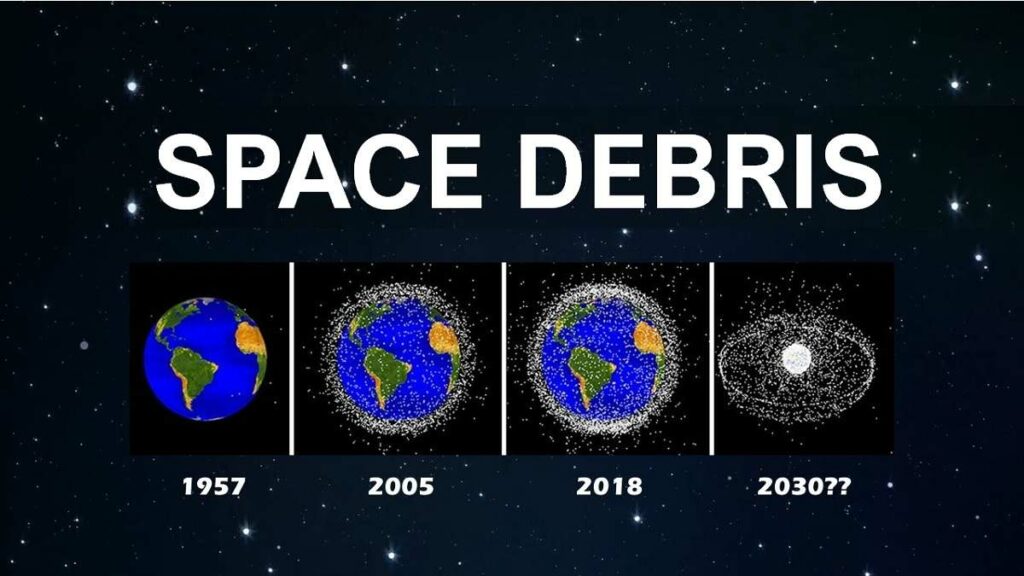
As humanity continues to explore and utilize space, an invisible but looming threat is becoming increasingly evident – space debris. This article delves into the science behind space debris, its origins, the dangers it poses, and the measures being taken to mitigate this cosmic hazard.
Space debris, also known as space junk, refers to the defunct human-made objects that are left floating in space. These objects can range from old satellites and spent rocket stages to fragments from collisions or explosions. With the increasing number of space missions and satellite launches, the amount of space debris has been steadily growing over the years.
1.2 The Origins of Space Debris
To fully grasp the magnitude and potential dangers associated with space debris, it is essential to delve into its origins. Space debris consists of a vast array of human-made and naturally occurring objects, which include not only defunct satellites and spent rocket stages but also minuscule meteoroids. The presence of such objects in Earth’s orbit can give rise to significant hazards that pose serious threats to both manned and unmanned spacecraft.
2. Understanding Space Debris
2.1 What is Space Debris?
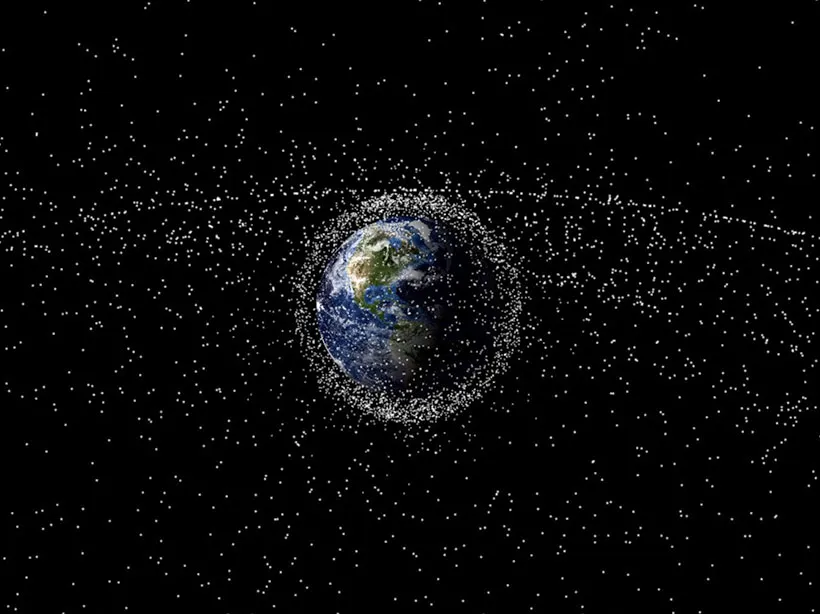
Space debris, also referred to as orbital debris or space junk, is a significant concern in Earth’s orbit. It encompasses both non-functional, man-made objects and naturally occurring micrometeoroids. These objects come in a wide range of sizes, with some being as small as tiny paint flecks, while others are as large as defunct satellites that can be as big as buses. It is worth noting that while certain debris is deliberately placed in orbit, a substantial amount of it is the result of previous space missions and activities.
2.2 The Lifecycle of Space Debris
Space debris follows a complex and intricate lifecycle that spans from the initial launch of satellites, rocket stages, and various other equipment into the vast expanse of space. As time passes, these objects, once crucial for various space missions, may eventually lose their functionality, adding to the ever-growing population of space debris. The presence of non-functional debris in orbit poses a significant challenge and threat to active satellites, as well as to other functioning debris in close proximity. The potential for collisions between space debris and operational satellites, or even between different debris objects, serves to intensify the magnitude of this problem, resulting in a cascading effect that compounds the challenges faced by space agencies and organizations in effectively managing and mitigating the risks associated with space debris.

3. The Dangers of Space Debris
3.1 Collisions in Orbit
One of the primary dangers of space debris is the risk of collision with operational satellites and spacecraft. This risk arises due to the large amount of debris present in Earth’s orbit. These debris can range from small fragments to larger objects, and even a small piece of debris can cause catastrophic damage when colliding with a satellite or spacecraft at orbital velocities. The consequences of such collisions can be severe, with potential outcomes including disabling communication satellites, disrupting important services that rely on satellite technology, and endangering the lives of astronauts aboard the International Space Station. Therefore, it is crucial to actively track and monitor space debris and implement measures to mitigate the risks associated with their presence in orbit.
3.2 The Kessler Syndrome
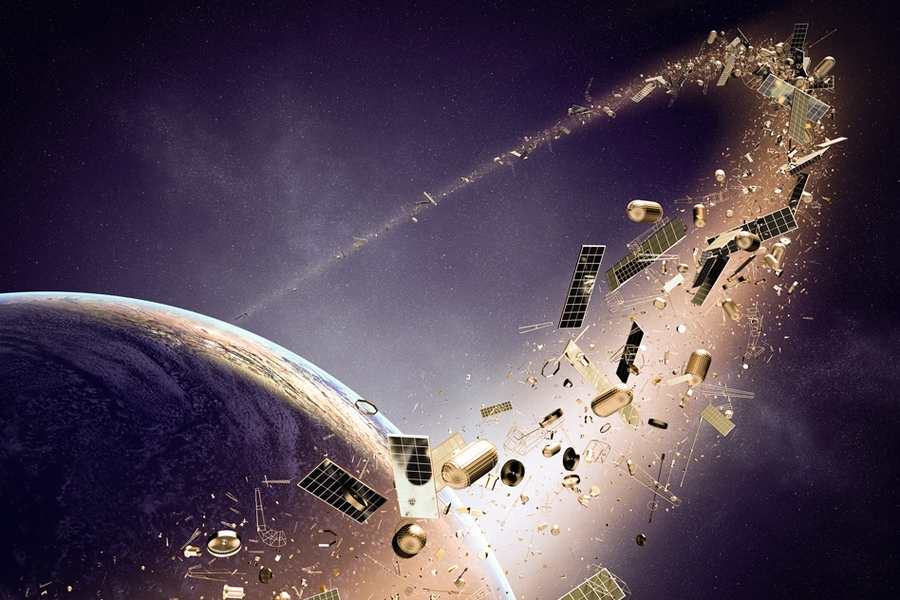
The Kessler Syndrome, originally proposed by NASA scientist Donald J. Kessler, is a highly alarming and catastrophic scenario in which a relentless series of collisions among space debris creates a dangerous chain reaction. As each collision occurs, it generates even more debris, thereby exponentially increasing the likelihood of subsequent collisions. This domino effect, if left unchecked, has the potential to render critical orbits in space completely unusable for an extended period of time, possibly lasting for centuries. Such a dire outcome would have severe and far-reaching consequences, significantly hampering and impeding various space activities and missions.
3.3 The Threat to Satellites
Satellites play a vital and indispensable role in our modern society. They are responsible for a wide range of important tasks, such as weather forecasting, global communications, and scientific research. The services they provide are invaluable and have become an integral part of our daily lives. However, these valuable assets are not without their vulnerabilities. One of the greatest threats they face is the presence of space debris. This debris, consisting of defunct satellites, spent rocket stages, and other fragments, poses a significant risk to the functionality and longevity of satellites. Collisions with space debris can result in catastrophic damage, rendering the satellites useless and disrupting the services they offer. Therefore, it is of utmost importance to implement effective measures and strategies to protect these satellites from such collisions. By doing so, we can ensure the continued operation and availability of the essential services that satellites provide, benefiting humanity in countless ways.
4. Mitigating Space Debris
4.1 Tracking and Monitoring
Space agencies and organizations worldwide play a crucial role in the constant monitoring and tracking of space debris. Their primary objective is to accurately predict and prevent potential collisions between debris and satellites by continuously adjusting the orbits of these valuable assets. To achieve this, highly sophisticated radar systems and powerful telescopes are employed to collect and analyze extensive data on the precise positions and intricate trajectories of various debris objects. This comprehensive approach ensures the safety and longevity of our satellite networks and promotes the sustainable utilization of outer space.
4.2 Deorbiting and Removal
To address the increasing problem of space debris and its potential risks to satellites and spacecraft, there are several ongoing initiatives aimed at actively removing defunct satellites and larger debris from orbit. These efforts involve the development and implementation of various innovative technologies and approaches. For instance, researchers are exploring the use of advanced harpoons, specialized nets, and even robotic spacecraft designed specifically for the purpose of debris removal. These initiatives are crucial in ensuring the long-term sustainability of space activities and preventing further accumulation of space debris, which could pose significant hazards to future space missions.
4.3 International Cooperation
The issue of space debris is a matter of significant global concern that demands urgent attention and calls for enhanced international cooperation. It is crucial for space agencies worldwide, including renowned organizations like NASA, ESA, and Roscosmos, to actively collaborate and engage in the sharing of vital data and the development of innovative strategies aimed at effectively mitigating the growing problem of space debris. Furthermore, international guidelines and agreements play a pivotal role in fostering responsible space activities and ensuring the long-term sustainability of outer space for future generations.

5. The Future of Space Debris
5.1 Space Sustainability
Ensuring space sustainability is not only essential but also crucial for the future of humanity. As we venture further into space exploration, it becomes increasingly important to prioritize the preservation and protection of our celestial environment. Achieving this goal requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses various strategies and initiatives.
One key aspect is the design and implementation of spacecraft with comprehensive disposal plans. By carefully considering the end-of-life stages of satellites and other space vehicles, we can minimize the accumulation of space debris and prevent potential collisions or accidents. This proactive approach ensures that our space endeavors do not contribute to the problem but instead promote long-term sustainability.
Another critical factor in space sustainability is the reduction of new debris creation. This involves employing innovative technologies and materials that are less prone to fragmentation or disintegration. By using robust and durable components, we can mitigate the risk of generating additional space debris during satellite launches or other space activities.
Furthermore, actively removing existing debris is paramount to maintaining a safe and navigable space environment. Through the deployment of specialized spacecraft equipped with advanced debris removal systems, we can target and eliminate defunct satellites, spent rocket stages, and other hazardous debris. This not only safeguards operational spacecraft but also reduces the overall density of space debris, making future space missions safer and more sustainable.
In conclusion, our commitment to space sustainability should be unwavering. By designing spacecraft with disposal plans, reducing the creation of new debris, and actively removing existing debris, we can ensure a safe and prosperous future in space exploration.
5.2 The Role of Space Agencies
Space agencies, such as NASA and ESA, play a crucial role in leading the way when it comes to space debris research and mitigation efforts. Their ongoing dedication to this important task is of utmost importance in ensuring the safety and sustainability of space activities. By actively studying and monitoring space debris, these agencies are able to identify potential risks and develop effective strategies to minimize their impact. Through international collaborations and advanced technologies, they are continuously working towards the goal of creating a cleaner and safer space environment for future generations.
5.3 Conclusion
Space debris, also known as orbital debris, refers to the collection of defunct objects in space, including old satellites, spent rocket stages, and fragments from collisions or explosions. The presence of space debris poses significant risks to current and future space missions, as well as to the safety of astronauts and valuable space assets.
To address this pressing issue, it is crucial to enhance our knowledge of space debris and its behavior. Scientists and engineers are actively studying the dynamics of space debris, such as its orbital patterns and the potential for collisions. By gaining a deeper understanding of these factors, we can develop effective strategies to safeguard our space infrastructure and ensure the sustainability of space activities.
In addition to scientific research, proactive measures are necessary to actively remove or mitigate space debris. Various approaches are being explored, including the deployment of space-based robots or satellites equipped with nets or harpoons to capture debris, as well as the use of lasers to alter the trajectory of larger objects. International cooperation is also vital in establishing guidelines and protocols for responsible space debris management.
Furthermore, public awareness and education play a crucial role in addressing the issue of space debris. By raising awareness about the potential consequences of uncontrolled space debris accumulation, we can encourage individuals, organizations, and governments to take responsible actions and contribute to the preservation of space for future generations.
In conclusion, the growing concern of space debris calls for immediate attention and proactive measures. By advancing our understanding of space debris, implementing effective removal strategies, and promoting public awareness, we can ensure the safety and sustainability of space exploration and utilization for the years to come.