The Remaining Lifespan of the Sun: A Cosmic Perspective
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- 1.1 The Sun: Our Life-Giving Star
- 1.2 The Sun’s Finite Existence
- The Sun’s Life Cycle
- 2.1 Birth of a Star
- 2.2 The Main Sequence
- 2.3 The Sun’s Current State
- The Sun’s Future Evolution
- 3.1 The Hydrogen Depletion
- 3.2 Expansion into a Red Giant
- 3.3 The Fate of Earth
- Measuring the Sun’s Remaining Lifespan
- 4.1 Stellar Models
- 4.2 The Sun’s Predicted Lifespan
- The Impact on Our Solar System
- 5.1 The Fate of Planets
- 5.2 The Search for a New Home
- 5.3 Conclusion
1. Introduction
1.1 The Sun: Our Life-Giving Star
The Sun, a bright and radiant celestial object composed of scorching hot, luminous gas located right at the heart of our vast solar system, serves as the ultimate origin of all living organisms on our beloved planet Earth. It generously bestows upon us an abundance of illumination, heat, and vital energy, thereby enabling the existence of life as we presently perceive it. However, just like its stellar counterparts, the Sun possesses a limited duration of existence, and gaining a comprehensive comprehension of its forthcoming destiny constitutes an indispensable component in comprehending the ultimate destiny that awaits our entire solar system.
1.2 The Sun’s Finite Existence
Although the Sun, our closest star, has been shining brightly for an astonishing 4.6 billion years, its brilliant radiance will not continue indefinitely. Like all stars in the universe, the Sun is destined to exhaust its nuclear fuel and embark on a mesmerizing journey of transformation. These incredible changes will have far-reaching consequences, impacting every celestial body within its gravitational reach. In this captivating article, we delve into the fascinating cosmic timeline of our beloved Sun, unraveling its majestic past and contemplating its awe-inspiring ultimate destiny.
2. The Sun’s Life Cycle
2.1 Birth of a Star
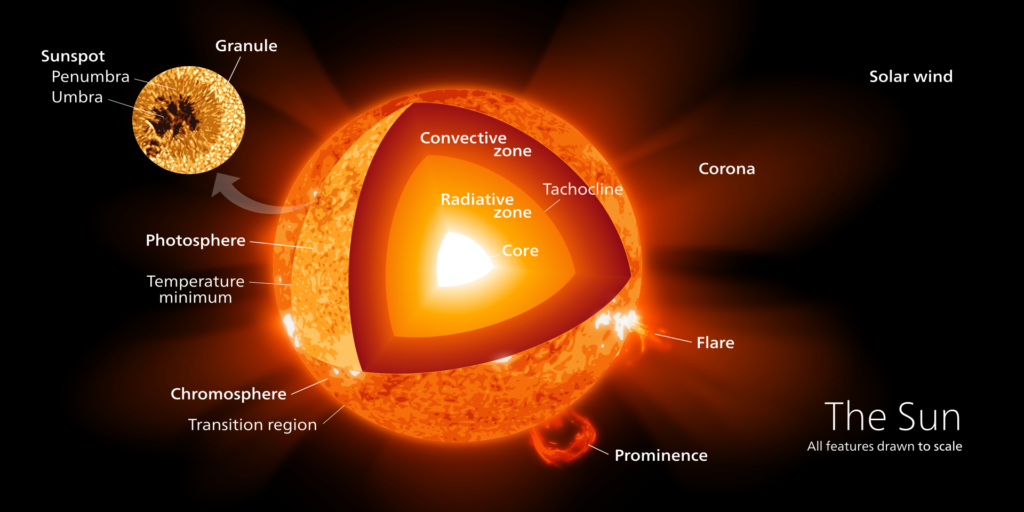
The Sun’s journey began billions of years ago in a vast, swirling cloud of gas and dust known as a molecular cloud. This massive cloud, under the relentless pull of gravity, gradually collapsed upon itself, giving birth to a dense core. As this core continued to accumulate matter, it experienced an increase in temperature and density, reaching a critical point where the unimaginable process of nuclear fusion was ignited, setting the Sun ablaze with its magnificent and awe-inspiring light.
2.2 The Main Sequence
Throughout the majority of its existence, the Sun has resided in the main sequence phase, a period characterized by the fusion of hydrogen atoms into helium within its core. This remarkable process unleashes an extraordinary quantity of energy, thereby fueling the Sun’s radiant luminosity and generating the heat that it emits.
2.3 The Sun’s Current State
As of now, the Sun is still in the main sequence phase. It has been shining steadily for billions of years, providing us with light and heat. The Sun’s incredible longevity is a testament to its vast reserves of hydrogen fuel, which have sustained it for such a long time. However, we must be aware that this fuel is not infinite, and the Sun is slowly undergoing changes as a result. These changes may have far-reaching implications for the future of our solar system and our planet. It is fascinating to ponder the eventual evolution of our Sun and what it may mean for life on Earth.

3. The Sun’s Future Evolution
3.1 The Hydrogen Depletion
The Sun’s primary source of energy is the nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium in its core. This incredibly powerful process involves the conversion of mass into energy, releasing an enormous amount of heat and light. As hydrogen is consumed in this fusion reaction, the core of the Sun gradually shrinks and becomes denser, causing an increase in temperature and pressure. This increase in temperature and pressure is what sustains the nuclear fusion reactions in the core, maintaining the Sun’s energy output. However, as the Sun’s core continues to shrink and heat up, it will eventually reach a critical point in its evolution. At this critical point, the Sun’s core will no longer be able to support the fusion reactions, and the Sun will undergo significant changes, marking a new phase in its life cycle.
3.2 Expansion into a Red Giant
As the core’s temperature and pressure continue to rise steadily over time, the Sun will experience profound transformations. Gradually, it will undergo a dramatic expansion, growing into a magnificent red giant. This phenomenal growth will cause the Sun to increase in size to such an extent that it will eventually engulf the inner planets, including our own planet Earth. This momentous event will undoubtedly represent a pivotal milestone in the life cycle of our beloved Sun, forever altering its course and shape.
3.3 The Fate of Earth
During the Sun’s red giant phase, which occurs towards the end of its life cycle, Earth will face a multitude of unprecedented challenges. These challenges will not only test the limits of our existence but also force us to reevaluate our understanding of life itself. As the Sun expands and engulfs Earth, temperatures will soar to unimaginable heights, rendering our planet inhospitable for life as we currently know it. The scorching heat will transform the once familiar landscape into a desolate and barren wasteland. However, amidst this catastrophic transformation, a breathtaking phenomenon will unfold. The outer layers of the dying star will be violently expelled, giving birth to a mesmerizing planetary nebula. This celestial spectacle, while awe-inspiring in its beauty, serves as a haunting reminder of the ephemeral nature of our existence and the relentless power of the cosmos.
4. Measuring the Sun’s Remaining Lifespan
4.1 Stellar Models
Astronomers rely on intricate stellar models to accurately forecast the progression of stars, including our very own Sun. These sophisticated models encompass a multitude of factors, encompassing but not limited to mass, composition, and age, in order to provide a comprehensive estimation of a star’s forthcoming behavior. By meticulously considering these crucial elements, astronomers are able to gain invaluable insights into the intricate workings and eventual fate of stars within the vast cosmos.
4.2 The Sun’s Predicted Lifespan
Based on current models and scientific estimates, it is fascinating to learn that the Sun, our very own star, still has approximately 5 billion years remaining in its main sequence phase. This phase, often described as the middle-aged stage in stellar terms, signifies that the Sun is far from reaching the end of its life cycle. However, it is interesting to note that the red giant phase, which follows the main sequence phase, will be relatively shorter in duration. As we ponder over the Sun’s future, we come to realize that its ultimate fate is already predetermined, leaving us in awe of the vastness and complexity of the universe.

5. The Impact on Our Solar System
5.1 The Fate of Planets
As the Sun undergoes a remarkable transformation into a red giant, the inner planets, including our beloved Earth, will be confronted with a multitude of daunting challenges. Inevitably, the scorching heat and powerful solar wind will relentlessly assail their delicate atmospheres, leaving them barren and devoid of any hospitable conditions for life as we know it.
5.2 The Search for a New Home
Humanity’s survival will heavily rely on the urgent quest to discover a new habitable world capable of sustaining human life beyond Earth’s limitations. As we face the imminent transformation of the Sun, it becomes increasingly crucial for us to not only search for alternative planets but also to invest in the development of cutting-edge technologies that can withstand the tremendous challenges posed by such an event. The exploration of exoplanets, which are celestial bodies orbiting stars outside our solar system, holds immense potential in our pursuit of finding a suitable home for future generations. Additionally, the concept of interstellar travel, the ability to journey between stars, may serve as a pivotal breakthrough in ensuring the survival and prosperity of humanity in the face of cosmic uncertainties.
5.3 Conclusion
The Sun, our beloved and awe-inspiring star, possesses a finite lifespan, which means that it will eventually undergo changes that will have far-reaching implications for our entire solar system and, in turn, for the very existence of our species. The exploration and comprehension of the cosmic timeline of the Sun are not only of immense scientific interest but also of utmost importance for the future trajectory of humanity. By delving into the mysteries of the Sun’s lifecycle, we gain invaluable insights into the forces that shape our universe and the potential challenges and opportunities that lie ahead for our civilization.